Completion Date:
Project Overview
Did you know the last decade was the hottest in 125,000 years?
Are you aware the world is losing 1.2 trillion tons of ice each year?
Do you know the 10 warmest years on record happened since 2010?
Well, these alarming facts are all linked to burning fossil fuels, the largest driver of global
climate change.
Once upon a time, humans discovered a miraculous source of energy - fossil fuels. They
saw these resources to propel themselves forward and create a better world for generations
to come. Little did they know that the use of fossil fuels would eventually lead to a global
climate crisis.
Fossil fuels: non-renewable, formed from ancient organisms, provide 80% of global energy,
crucial for progress in technology, society, and economics.
However, World's dependence on fossil fuels is contributing to the acceleration of climate
change and have negative impacts on the environment, including air and water pollution,
greenhouse gas emissions, melting of polar ice caps and glaciers, rising sea levels, ocean
acidification, and health problems leading to millions of premature deaths each year.
Role:
Problem Statement
According to International Energy Agency, global fossil fuel energy production increased by
approximately 59% and consumption increased by approximately 46% between 2001 and
2019. The challenge is to reduce global dependence on fossil fuels, transition to cleaner and
renewable energy sources, and address the social, economic, and environmental
consequences of the fossil fuel industry. Governments, businesses, and individuals all have
a role to play in promoting the transition to cleaner energy sources.
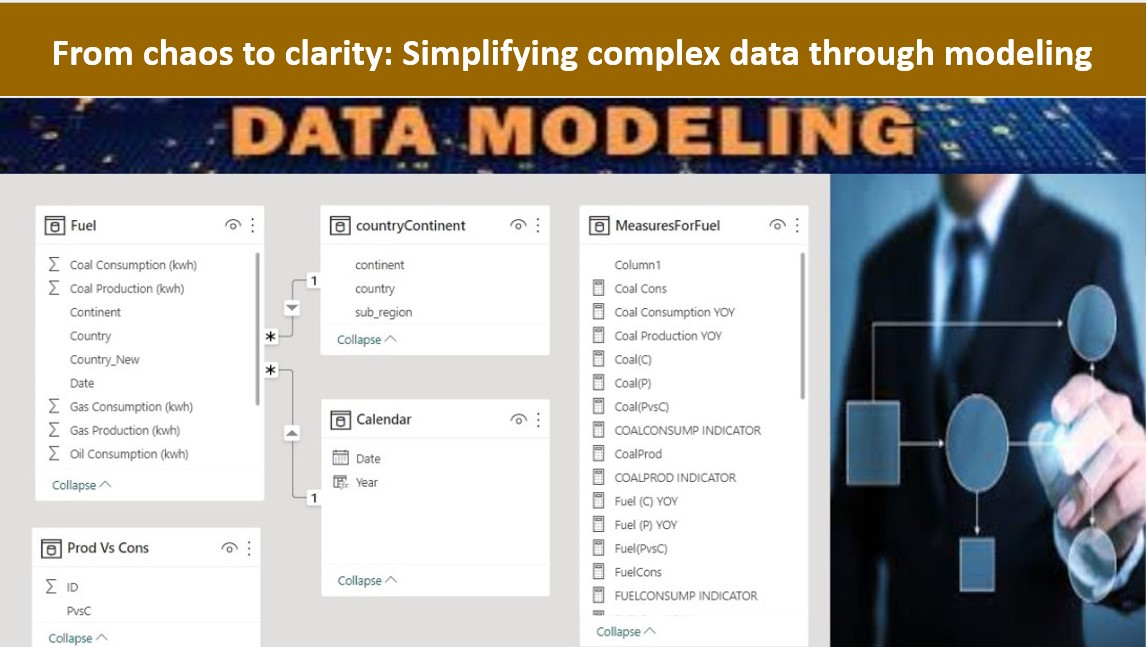
My project provides a comprehensive analysis of global fossil fuel energy production and
consumption. The top producers of fossil fuels are China, the United States, Russia, Saudi
Arabia, and India, while the largest consumers are China, the United States, Russia, India,
and Japan. These countries have significant reserves of fossil fuels and expanding
economies that require high energy consumption.